

But NEMA also builds in a safety factor, primarily to account for hot spots-i.e., parts of the motor winding that may be hotter than the location at which the temperature is measured.

Since the maximum ambient temperature according to NEMA MG 1-2003 is normally 40 C, one would expect the temperature rise limit for a Class B system to be 90 C (130 C – 40 C). For example, a Class B insulation system is rated 130 C, while a Class F system is rated 180 C. NEMA rates insulation according to its ability to withstand overall temperature. The difference between the ambient temperature and that of a motor operating under load is the temperature rise (temperature rise = hot temperature – ambient temperature). Once the temperature rating is known, the temperature rise can be measured directly using sensors or an infrared temperature detector, or indirectly using the resistance method.Īmbient temperature is the temperature of the air (or other cooling medium) that surrounds the motor.
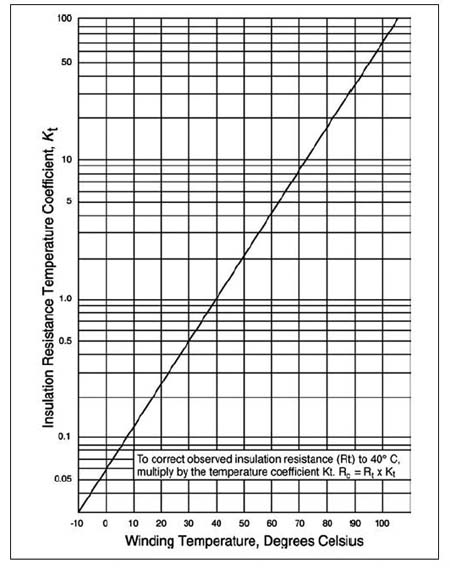
Temperature rating also can be found on the motor’s original nameplate. The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) defines this rating for three-phase induction motors in its standard Motors and Generators, MG 1-2003. The first step to prevent unexpected shutdowns and extend motor life is to determine the temperature rating of the motor. But it is easy to forget that exceeding the rated operating temperature by as little as 10 C (18 F) can shorten the life of a three-phase induction motor by half. It is no secret that heat kills electric motors. Regularly checking the operating temperature of each critical motor will pay dividends.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
